HA injections can help your patient’s OA knee pain—but not all are created equal2-3
– Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
Molecular Weight
- Intra-articular (IA) injections of high molecular weight, single-chained HA induce the body to naturally synthesize its own high molecular weight HA.2,9
- Repeat exposure to high molecular weight HA may improve how the synovial fluid distributes throughout the knee—improving the joint’s ability to produce its own HA.9-11
Structure

Linear/Single-chained HAs12
Most closely resemble natural HA found in the knee
Help with reducing knee joint inflammation
Cross-linked HAs12,13
May use formaldehyde and vinyl sulfone during chemical modification of HA
May increase the likelihood of joint inflammation
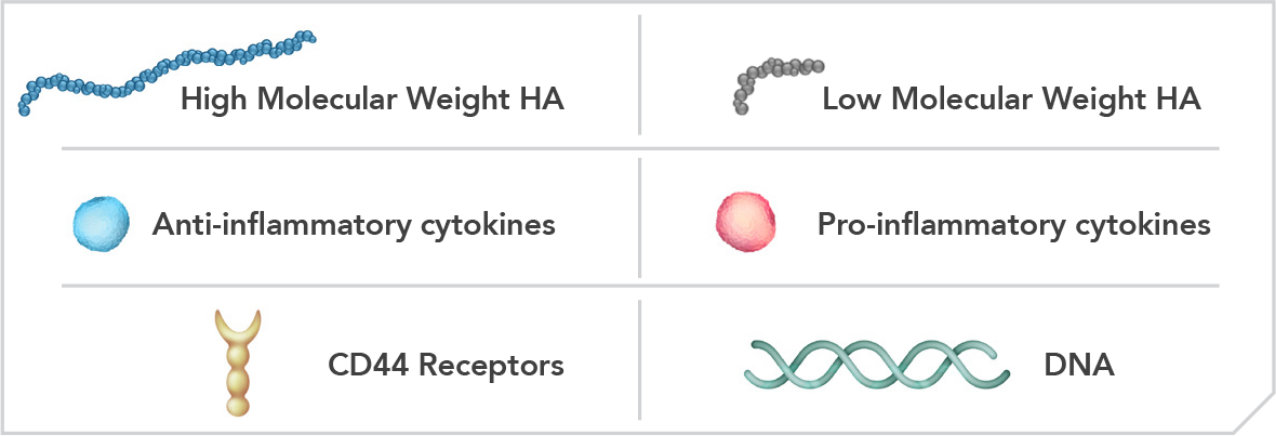
High molecular weight linear HA exerts anti-inflammatory effects by binding to CD44 receptors and limiting cytokine production.12,14
Anti-Inflammatory12,14

High Molecular Weight Linear HA
Binds to CD44 receptors PROMOTING activation of ANTI-INFLAMMATORY cytokine production
Successfully binding to CD44 receptors helps14:
- Reduce pain and inflammation
- Protect cartilage
- Create more HA which is naturally found in the body
Pro-Inflammatory12,14

Low Molecular Weight Linear HA
Binds suboptimally to CD44 receptors PROMOTING PRO-INFLAMMATORY cytokine production
OPTION FOR OA KNEE PAIN
When it comes to OA of the knee, the right treatment can make all
the difference. Discover how some treatment options can help your
patient’s OA knee pain in more ways than one.
Dual-Acting Effects
Find out how EUFLEXXA may help your patients’ OA knee pain in two ways.
Discover the Effects- Rolling 12 month average of IQVIA claims data based on unique patients (December 2022).
- Altman R, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of intra-articular hyaluronic acid: a systematic review. Cartilage. 2019;10(1):43-52.
- Altman RD,
Manjoo A, Fierlinger A, et al. The mechanism of action for hyaluronic acid treatment in the osteoarthritic knee: a systematic review. BMC Musculoskelet Disor. 2015;16:321. - Food and Drug Administration. Federal Register. 2018;83:242.
- Balazs EA, The physical properties of synovial fluid and the special role of hyaluronic acid. In: Helfet AJ. Disorders of the Knee. Pages 63–75. Philadelphia: Lippincott Company, 1974.
- Liao Y-H, Jones SA, Forbes B, et al. Hyaluronan: pharmaceutical characterization and drug delivery. Drug Delivery. 2005;12:327–342. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/10717540590952555%20
- Moreland LW. Intra-articular hyaluronan (hyaluronic acid) and hylans for the treatment of osteoarthritis: mechanisms of action. Arthritis Res Ther. 2003;5:54-67.
- Bahrami M, et al. Efficacy of single high-molecular-weight versus triple low-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid intra-articular injection among knee osteoarthritis patients. BMC Musculoskelet Disor. 2020;21:550.
- Smith MM, Ghosh P. The synthesis of hyaluronic acid by human synovial fibroblasts is influenced by the nature of the hyaluronate in the extracellular environment. Rheumatol Int. 1987;7:113-122.
- Concoff A, Sancheti P, Niazi F, Shaw P, Rosen J. The efficacy
of multiple versus single hyaluraonic acid injections: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disor.
2017 Dec 21;18(1):542. doi:10.1186/s12891-017-1897-2 - Loknauth J, Driscoll KE, Bendele A, Niazi F, Liang A, Larsen CC. Viscosupplementation may preserve tibial cartilage and collagen in osteoarthritis: findings from a preclinical model
of osteoarthritis. J Exp Orthop. May 31, 2020;7(1):39. doi:10.1186/s40634-020-00256-4 - Nicholls M, et al. A comparison between rheological properties of intra-articular hyaluronic acid preparations and reported human synovial fluid. Adv Ther. 2018;35:523-530.
- Goldberg V, Coutts R. Pseudoseptic reactions of hylan viscosupplementation. Clin Orthop. 2004;
419:130-137. - Yang C, Cao M, Liu H, et al. The high and low molecular weight forms of hyaluronan have distinct effects
on CD44 clustering. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(51):43094-43107.


